Download
Beta Release
ueforth-pico-ice-7.0.7.22.zip
Version: 7.0.7.22 (Beta)
Release Archive - Prior Releases
http://github.com/flagxor/ueforth - Complete Unprocessed Source Code
License
NOTE: Although ueforth is licensed under Apache 2.0, please be aware that binaries are built with SDKs that include other licenses including MIT, Raspberry Pi License, and possibly others. Be sure to consult a lawyer before using for comercial purposes.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Install
- Connect your pico-ice to USB.
- Connect the USB_BOOT pin to ground.
- Press reset on the pico-ice.
- Copy ueforth-pico-ice.uf2 to the mounted drive.
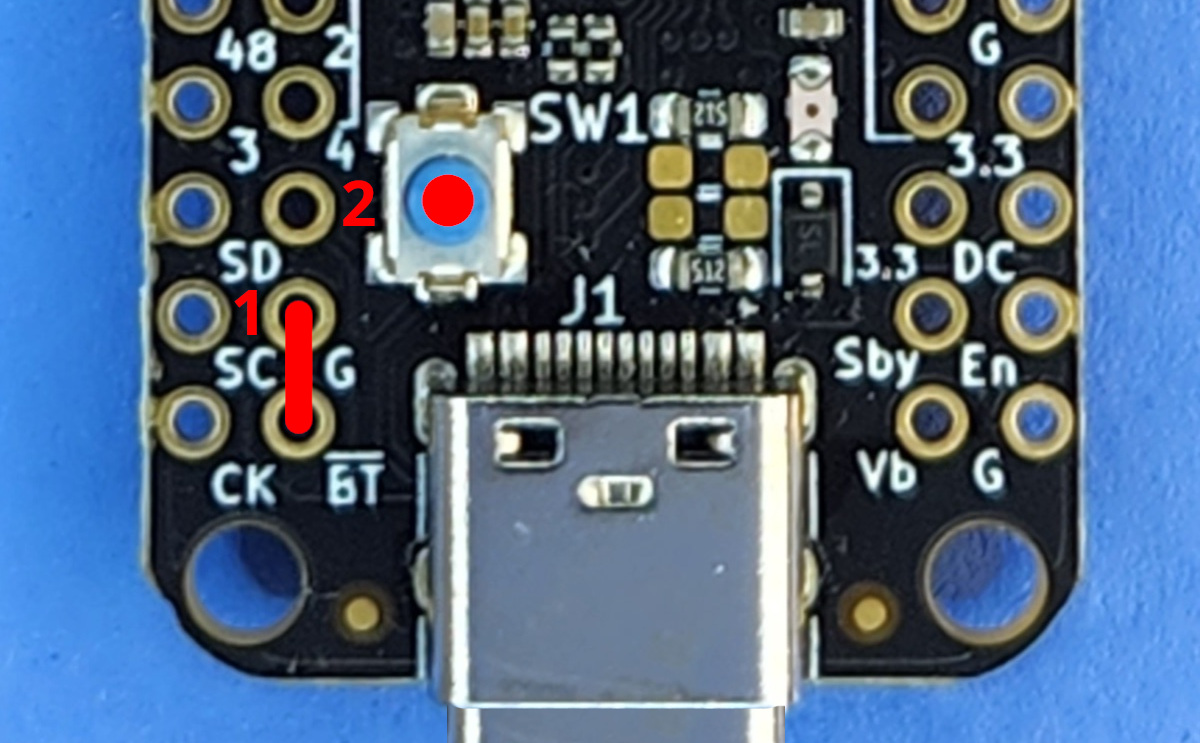
See detailed instructions for MCU programming
Use
Initially µEforth can be interacted with over a serial port (over USB).
One popular option is to use the serial port option on
PuTTY.
Be sure to config the serial port to: baud rate = 115200, data bits = 8, stop bits = 1, and parity = N.
pico-ice Features
pico-ice Words
Null Terminated Strings
As null terminated strings are used throughout C interfaces, their use is supported in Forth by way of several non-standard words with the convention of using Z/z to refer to such strings in names and stack comments.
Z" ( "string" -- z ) Creates a null terminated string on the heap Z>S ( z -- a n ) Convert a null terminated string to a counted string S>Z ( a n -- z ) Conver a counted string string to null terminated (copies string to heap)
Raw Strings
Raw strings are provided better support using a string for the duration of the current command, without consuming heap memory.
R" ( "string" -- a n ) Creates a temporary counted string R| ( string| -- a n ) Creates a temporary counted string ending with |
Utilities
DUMP ( a n -- ) Dump a memory region SEE ( "name" -- ) Attempt to decompile a word VARIABLE ECHO -- Determines if commands are echoed REMAINING ( -- n ) Bytes remaining in Forth heap. DUMP-FILE ( data data# fn fn# -- ) Write contents of a file throws on error.
Vocabularies
uEForth uses a hybrid of Forth-79 and Forth-83 style vocabularies.
By default vocabularies chain to the vocabulary in which they were defined,
as in Forth-79. However, like Forth-83, ALSO
can be used to add vocabularies to a vocabulary stack of which
CONTEXT @ is the first item.
The word ONLY clears the vocabulary stack, but as there is
no separate ONLY vocabulary, it also sets CONTEXT
to the FORTH vocabulary.
The word SEALED modifies the most recently defined vocabulary
such that it does not chain. Note, this must be done before words are added to it.
VOCABULARY ( "name" ) Create a vocabulary with the current vocabulary as parent
FORTH ( -- ) Make the FORTH vocabulary the context vocabulary
DEFINITIONS ( -- ) Make the context vocabulary the current vocabulary
VLIST ( -- ) List the words in the context vocabulary (not chains)
WORDS ( -- ) List the words in the context vocabulary (including chains)
TRANSFER ( "name" ) Move a word from its current dictionary to the current vocabulary
Useful for "hiding" built-in words
TRANSFER{ ..words.. }TRANSFER ( -- ) Transfer multiple words to the current vocabulary
ALSO ( -- ) Duplicate the vocabulary at the top of the vocabulary stack
PREVIOUS ( -- ) Drop the vocabulary at the top of the vocabulary stack
ONLY ( -- ) Reset context stack to one item, the FORTH dictionary
Non-standard, as there's no distinct ONLY vocabulary
ORDER ( -- ) Print the vocabulary search order
SEALED ( -- ) Alter the last vocabulary defined so it doesn't chain
Interpret Time Conditions
[IF], [ELSE], and [THEN] can be used
to selectively compile. Used in tandem with DEFINED? they can
be used to handle the absence of modules gracefully.
Nesting is supported.
DEFINED? ( "name" -- xt|0 ) Check if a word exists (works at compile time too). [IF] ( f -- ) Conditionally interpret the text the follows. [ELSE] ( -- ) Interpret time ELSE. [THEN] ( -- ) Interpret time THEN.
Floating-Point
Requires v7.0.6.5+
Single precision floating-point support is available as a work in progress. While initially left out in the name of minimalism, hardware support for floating-point argues some advantages to limited support.
Floating point is kept on a separate stack.
NOTE: Tasks currently don't correctly support floating point. A single floating point stack is shared by all tasks.
FLOAT OPCODES ------------- DOFLIT ( --- ) Puts a float from the next cell onto float stack. FP@ ( -- a ) FP! ( a -- ) SF@ ( a -- r ) Single precision load SF! ( r a -- ) Single precision store FDUP ( r -- r r ) FNIP ( ra rb -- rb ) FDROP ( r -- ) FOVER ( ra rb -- ra rb ra ) FSWAP ( ra rb -- rb ra ) F0< ( r -- f ) F0= ( r -- f ) F+ ( r r -- r ) F- ( r r -- r ) F* ( r r -- r ) F/ ( r r -- r ) 1/F ( r -- r ) S>F ( n -- r ) F>S ( r -- n ) HIGH LEVEL ---------- F= ( r r -- f ) F< ( r r -- f ) F> ( r r -- f ) F<= ( r r -- f ) F>= ( r r -- f ) F<> ( r r -- f ) SFLOAT ( -- 4 ) SFLOATS ( n -- n*4 ) SFLOAT+ ( a -- a+4 ) SF, ( r -- ) AFLITERAL ( r -- ) FLITERAL ( r -- ) IMMEDIATE FCONSTANT ( r "name" ) FVARIABLE ( "name" ) PI ( -- r ) FSQRT ( r r -- r ) F.S ( -- ) Print float stack.
Locals
Locals allow named word local parameters and values.
Syntax:
{ local1 local2 .. -- comment }
or
{ local1 local2 .. }
Locals are ordered to match the stack, examples:
: 2OVER { a b c d } a b c d a b ;
: MAX { a b -- biggest } a b < IF b ELSE a THEN ;
( Equivalent with DO and FOR )
: POW2 { n } 1 { s } n FOR AFT s 2* to s THEN NEXT s ;
: POW2 { n } 1 { s } n 0 DO s 2* to s LOOP s ;
Capabilities and limitations:
- Support for locals referenced inside DO and FOR loops - OK
- Support for multiple {} uses in one definition - OK
- Support for TO and +TO to modify a local
- Locals mixed with raw return stack operations (
>R R>) - NOT OK - Locals defined inside a DO or FOR loop - NOT OK
- The low level ANSForth word
(LOCAL)is also supported.
pico-ice Bindings
Allocation
These words are inside theinternals vocabulary.
MALLOC ( n -- a | 0 ) System malloc SYSFREE ( a -- ) System free REALLOC ( a n -- a | 0 ) System realloc
System
MS ( n -- ) Pause for some number of milliseconds. MS-TICKS ( -- n ) Time since start in milliseconds. TERMINATE ( n -- ) Call system exit.
Files
R/O ( -- mode ) R/W ( -- mode ) W/O ( -- mode ) BIN ( mode -- mode ) CLOSE-FILE ( fh -- ior ) OPEN-FILE ( a n mode -- fh ior ) CREATE-FILE ( a n mode -- fh ior ) DELETE-FILE ( a n -- ior ) WRITE-FILE ( a n fh -- ior ) READ-FILE ( a n fh -- n ior ) FILE-POSITION ( fh -- n ior ) REPOSITION-FILE ( n fh -- ior ) FILE-SIZE ( fh -- n ior )
pico
These words are inside thepico vocabulary.
See here
for details on the underlying hardware SDK.
adc_init ( -- ) Initialize HW ADC adc_gpio_init ( n -- ) Init GPIO for use as ADC adc_select_input ( n -- ) Select ADC input adc_get_selected_input ( -- n ) Get selected ADC input adc_set_round_robin ( mask -- ) Round robin sampler selector adc_set_temp_sensor_enabled ( f -- ) Enable/disable onboard tempurature sensor adc_read ( -- u ) Perform a single conversion adc_run ( f -- ) Enable/disable free-running sample mode adc_set_clkdiv ( f: clkdiv -- ) Set ADC clock divisor adc_fifo_setup ( en dreq_en dreq_thresh err_in_fifo byte_shift -- ) Setup ADC FIFO adc_fifo_is_empty ( -- f ) Check FIFO empty state adc_fifo_get_level ( -- n ) Get number ADC FIFO entries adc_fifo_get ( -- n ) Get ADC result from FIFO adc_fifo_drain ( -- ) Drain FIFO. adc_fifo_get_blocking ( -- n ) Wait for ADC to have data adc_irq_set_enabled ( f -- ) Enable/disable ADC interrupts
ice
These words are inside theice vocabulary.
See here
for details on the underlying SDK.
ice_cram_open ( -- ) Open FPGA config RAM connection.
ice_cram_write ( a n -- ) Write bytes to the FPGA config RAM connection.
ice_cram_close ( -- ) Close FPGA config RAM connection.
ICE_FLASH_PAGE_SIZE ( -- n ) Get the size of a flash page.
ice_flash_init ( -- ) Init flash connection.
ice_flash_read ( addr a n -- ) Read from a flash address to a buffer.
ice_flash_erase_sector ( n -- ) Erase a flash sector.
ice_flash_program_page ( addr a -- ) Program a flash page.
ice_flash_erase_chip ( -- ) Erase whole flash.
ice_flash_wakeup ( -- ) Wakeup flash.
ice_flash_sleep ( -- ) Put flash in sleep mode.
ice_fpga_init ( n -- ) Init FPGA to a clock speed in MHz.
Valid inputs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 48
ice_fpga_start ( -- ) Start FPGA.
ice_fpga_stop ( -- ) Stop FPGA.
ice_led_init ( -- ) Initialize LED.
ice_led_red ( f -- ) Set on/off state of led red channel.
ice_led_green ( f -- ) Set on/off state of led green channel.
ice_led_blue ( f -- ) Set on/off state of led blue channel.
ice_spi_init ( -- ) Initialize SPI.
ice_spi_init_cs_pin ( cs_pin active_high -- ) Init selecting more options.
ice_spi_chip_select ( n -- ) Set csn_pin to assert.
Also set the SPI TX and SCK pins to output/drive mode,
and keeps the RX pin to input/high-z mode.
ice_spi_chip_deselect ( n -- ) Set csn_pin to assert.
Also set the SPI TX and SCK pins back to input/high-z mode.
ice_spi_read_blocking ( a n -- ) Read from SPI into buffer.
ice_spi_write_blocking ( a n -- ) Write to SPI from buffer.
ice_sram_init ( -- ) Initialize SRAM.
ice_sram_get_id ( a -- ) Read SRAM id into 8 byte buffer.
ice_sram_read_blocking ( addr a n -- ) Read from address in SRAM to memory.
ice_sram_write_blocking ( addr a n -- ) Write from memory to SRAM.